Overview
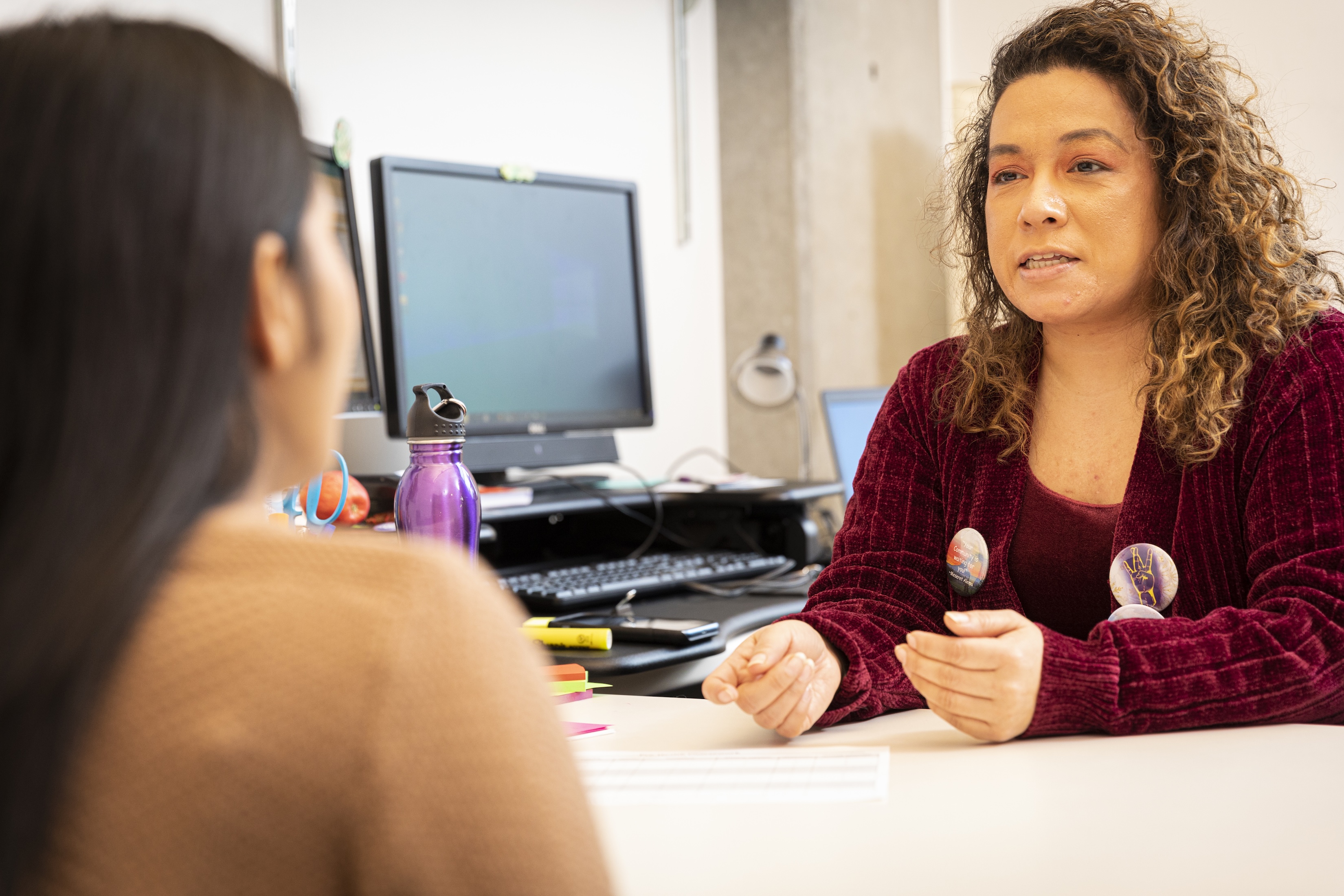
A career in genetic counseling can take a number of different directions. Many genetic counselors work in clinics assessing patients for their risk of having a genetic condition. These genetic counselors collect the personal and family medical histories from their patients, create family pedigrees, perform risk assessments, discuss testing options, order genetic testing, interpret genetic test results, and provide psychosocial counseling to help support patients as they decide the best course of action for themselves.
A Variety of Roles and Settings
Because of their specialized training in genetics and counseling, genetic counselors are uniquely equipped to fill a variety of professional roles. In addition to clinical genetic counseling, there are career opportunities in genetic testing laboratories, research and public health systems. Each setting has its own unique application of genetics and relies on its genetic counselors for their expertise in understanding and distilling complex genetic information and communicating it in a clear and concise way.
Career Outlook
The career outlook for genetic counselors is strong. The number of jobs is projected to grow by 26% between 2020 and 2030, according to the U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics.
According to the National Society of Genetic Counselors 2024 Professional Status Survey, the average starting salary for new graduates in full-time positions was $81,373. The average yearly gross salary for genetic counselors was $106,306.
Becoming a Genetic Counselor
To become a genetic counselor, you must first earn a master’s degree from an accredited genetic counseling program. In the United States, genetic counseling programs are accredited by the Accreditation Council for Genetic Counseling. After graduating from an ACGC-accredited program, you’ll be eligible to apply to take the American Board of Genetic Counseling certification examination. You’ll become a certified genetic counselor once you pass the board exam.
You may need to become licensed in order to practice as a genetic counselor in some states. The state where you intend to practice is the best source of information about licensure regulations. The National Society of Genetic Counselors maintains information on state licensure, and the Washington State Department of Health has details about Washington licensure.
genetic counseling resources
Want to learn more about a career in genetic counseling? Many genetic counselors are members of the National Society of Genetic Counselors, a professional organization dedicated to promoting the interests of genetic counselors. NSGC has many resources on its website, including an overview and a timeline of the genetic counseling profession. You may also want to check out the Pre-GC Series hosted by Columbia University.